What is a fiber media converter?
A media converter, also referred to as a fiber media converter, is a network device that facilitates the connection between two different media types, such as twisted pair and fiber optic cabling. Its fundamental purpose is to extend the transmission distance of a network by converting electrical signals (copper) into optical signals (fiber). These devices play a critical role in modern networks by ensuring compatibility and seamless integration between traditional wired systems and advanced high-speed fiber optic technologies. Available in various physical sizes and supporting diverse data transfer rates, media converters serve as multifunctional tools for expanding and maintaining network infrastructure.
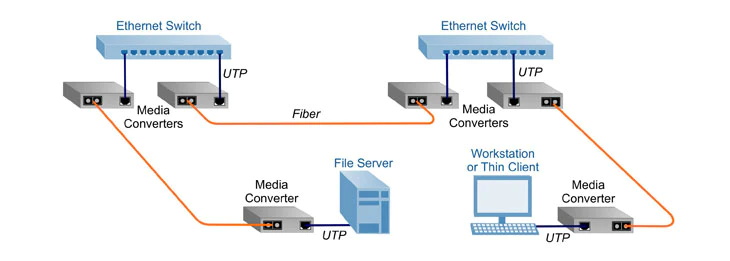
Advantages of media converters
1. Extended Communication Distance
Media converters significantly expand the coverage range of a network by converting electrical signals from copper cables into optical signals transmitted through fiber optic cables, which enables data to be transmitted over longer distances without compromising signal quality.
2. Cost-Effectiveness
Media converters simplify the incorporation of various network types and technologies, enabling a seamless shift from traditional copper-based networks to advanced fiber optic networks, which streamlines the process of expanding or upgrading your network while leveraging your existing wiring infrastructure, eliminating the need for a complete overhaul.
3. Enhanced Security
Optical fiber connections are less susceptible to electromagnetic interference (EMI) and eavesdropping compared to copper cables. By converting to a fiber optic network using media converters, overall security can be improved.
4. Flexibility and Scalability
Media converters are versatile devices, these devices can be used to connect different types of network media, including copper to fiber, multimode to single-mode, or one type of fiber to another. Additionally, media converters have a compact and easy-to-deploy design, allowing you to quickly add new devices to expand your network.
How to choose a fiber media converter?
1. Rate
The rate refers to the data transfer speed supported by the fiber media converter. It is typically measured in terms of data rate, such as Megabits per second (Mbps) or Gigabits per second (Gbps). The required rate depends on the network’s bandwidth needs and the applications being supported. Consider factors such as the volume of data traffic, future scalability, and compatibility with existing network infrastructure.
2. Fiber Type
Different fiber media converters support specific types of optical fiber, such as single-mode or multi-mode. Single-mode fibers transmit signals over longer distances with lower signal loss, making them suitable for long-haul transmissions. Multi-mode fibers are ideal for shorter distances and high-bandwidth applications within a confined area. Select a fiber media converter that is compatible with the fiber type used in your network.
3. Wavelength
The wavelength of the fiber media converter determines the specific frequency of light used for data transmission. Common wavelengths include 850nm, 1310nm, and 1550nm. The choice of wavelength depends on the fiber type and the network requirements. Make sure the transceiver’s wavelength matches your network infrastructure to ensure optimal performance and compatibility.
4. Fiber Port
The fiber port type refers to the physical connector interface used to connect the media converter to the optical fiber. Common fiber port types include SC, LC, and ST connectors. Consider the existing fiber connectors in your network and choose a media converter with a compatible port type to ensure seamless integration and reliable connectivity.
5. Transmission Distance
The transmission distance indicates the maximum reach of the fiber media converter. It is crucial to select a media converter that can support the required distance in your network infrastructure. Factors such as signal attenuation, dispersion, and signal quality should be considered when determining the appropriate media converter for the desired transmission distance.
6. Power over Ethernet (PoE)
The Power over Ethernet (PoE) function enables the media converter to receive power through the Ethernet cable, eliminating the need for separate power cables. It is particularly beneficial in applications where power sources are limited or difficult to access. Determine if your network requires PoE support and choose a media converter that meets those power requirements.
7. Power Supply Requirement
Consider the power requirements of the fiber media converter, including the type of power source—direct current (DC) or alternating current (AC). Determine whether your network infrastructure provides DC or AC power and select a media converter that is compatible with the available power source. Additionally, consider factors such as voltage levels and power consumption. Ensure that the power supply in your network can adequately support the transceiver’s power needs. What’s more, consider factors such as power redundancy and backup options for critical applications.
8. Unmanaged or Managed
Decide whether you need an unmanaged or managed fiber media converter. Unmanaged media converters are plug-and-play devices without advanced configuration options, ideal for simple network setups. Managed media converters offer additional features such as remote management, monitoring, and configuration capabilities. Evaluate your network management requirements to choose the appropriate type of fiber media converter.
9. Commercial or Industrial Grade
Consider the environmental conditions in which the fiber media converter will operate. Commercial-grade media converters are suitable for standard office environments, while industrial-grade media converters are designed to withstand harsh conditions such as extreme temperatures, moisture, and vibrations. Select a media converter that matches the environmental conditions of your deployment location.
Conclusion
Selecting fiber media converters requires careful consideration of various factors to ensure optimal performance, compatibility, and reliability. By evaluating these factors, you can make informed decisions that align with your network requirements. Taking the time to assess these factors will help you choose the right fiber media converters for your specific application.


