Plesiorhythmical Division Multiplexing (PDH) and Synchronous Digital Hierarchy (SDH) are 2 commonly used technologies for multiplexing and transporting digital signals in telecommunications networks. PDH and SDH have advantages and disadvantages, they are used in different scenarios depending on the network’s specific needs. In this article, we’ll look at PDH and SDH and compare their differences and similarities to help you understand which technology might be the best choice for your network.
What is the PDH?
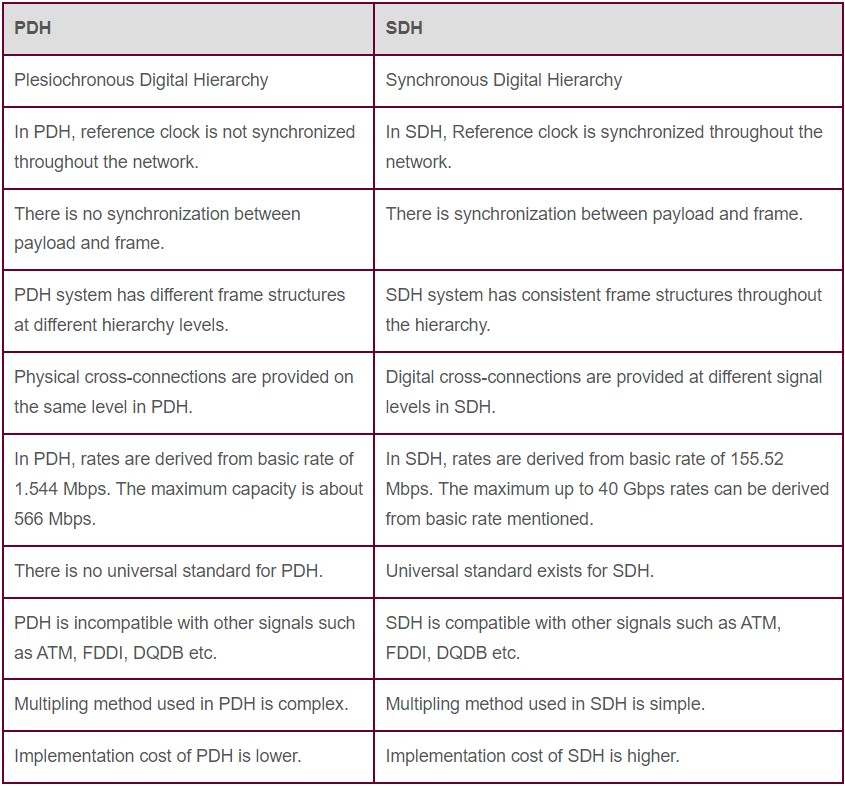
Plesiochronous Digital Hierarchy (PDH) is a telecommunication technology used for several decades. It is based on a plesiochronous timing system, which means that the clock rates of various devices in a network can slightly differ. This characteristic allows for the use of simpler and more cost-effective equipment. However, it also limits the maximum number of channels that can be multiplexed together due to these timing discrepancies.
PDH systems employ a technique known as bit interleaving to combine multiple lower-speed data channels into a single higher-speed channel. This process involves alternating the placement of bits from each lower-speed channel into the higher-speed stream, effectively interleaving them to maintain a steady flow of data.
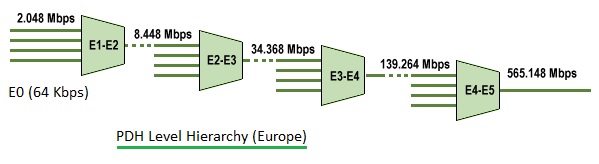
The PDH standards define several levels of data rates and multiplexing capabilities, including 2 Mbps (E1), 8 Mbps (E3), and 34 Mbps (E4). Each level represents an increment in the bandwidth capacity, allowing for more data to be transmitted simultaneously over a single communication line.
This technology, while somewhat outdated by more advanced systems like Synchronous Digital Hierarchy (SDH) and Optical Transport Networks (OTN), continues to be relevant in certain applications where high-cost infrastructure changes are not feasible.
What is the SDH?
Synchronous Digital Hierarchy (SDH) is an advanced telecommunications standard designed to overcome the limitations inherent in the older Plesiochronous Digital Hierarchy (PDH). At its core, SDH operates on a synchronous timing framework, ensuring that all devices within the network are precisely synchronized to a unified clock source. This synchronization dramatically increases network efficiency, enabling the simultaneous multiplexing of a more considerable number of channels and optimizing bandwidth utilization.
SDH employs a byte interleaving technique for multiplexing, which arranges bytes from multiple lower-speed channels into a higher-speed channel in a round-robin fashion. This method not only facilitates a seamless combination of data streams but also enhances error correction capabilities and simplifies system management.
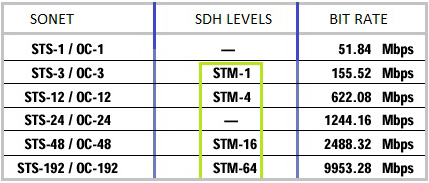
The SDH infrastructure is characterized by a set of standardized transmission rates, including 155.52 Mbps (STM-1), 622.08 Mbps (STM-4), and 2.5 Gbps (STM-16), among others. Each level, known as the Synchronous Transport Module (STM), reflects a hierarchical structure that provides scalability and supports the evolution of the network.
Furthermore, SDH’s architecture promotes a higher degree of interoperability between different vendors’ equipment and simplifies network upgrades and maintenance. By using overhead bytes for management and error-checking, SDH networks offer robust monitoring and improved fault isolation, resulting in superior network reliability and performance.
The introduction of SDH has marked a significant evolution in network transport, enabling the development of high-capacity backbone networks that are the foundation of modern telecommunications systems, including those supporting Internet and mobile services.
Differences between PDH and SDH
One of the principal distinctions between PDH (Plesiochronous Digital Hierarchy) and SDH (Synchronous Digital Hierarchy) lies in their network capacities and flexibility. PDH is typically employed in smaller-scale networks where bandwidth demands are modest. It operates at various capacity levels, extending up to the E4 level, which supports a bandwidth of about 140 Mbps, and in some systems even up to E5 level, offering capacities of around 565 Mbps. These levels accommodate more multiplexed channels, with E4 and E5 allowing for more data throughput than E3. In contrast, SDH is engineered to accommodate the expansive and intensive bandwidth needs of large-scale networks. It supports various hierarchical levels, such as STM-64 and STM-256. STM-64 can multiplex up to 4032 E1 channels, offering a substantial bandwidth of approximately 10 Gbps. At a higher tier, STM-256 further extends the capacity, capable of supporting around 40 Gbps. This scalability makes SDH ideal for high-capacity backbone networks and critical infrastructure requirements, where high data throughput and reliability are paramount.
The cost and complexity of equipment also diverge markedly between the two technologies. PDH infrastructure, with its limited functionality, tends to be more economical and simpler to deploy and maintain. This makes it a cost-effective solution for certain applications that don’t require the vast scalability and performance capabilities of SDH. However, for more dynamic and larger networks, the higher initial expenditure on SDH equipment is often justified by its superior performance and adaptability.
Furthermore, resilience and fault management are areas where PDH and SDH significantly differ. SDH has been designed with inherent robustness, employing redundancy schemes such as 1+1 protection and ring architectures to provide continuity of service despite equipment failures or network disruptions. This makes SDH networks exceptionally fault-tolerant, and capable of executing swift failover procedures that ensure minimal service interruption, often on the order of milliseconds.
PDH, by comparison, lacks these sophisticated mechanisms for fault tolerance and network recovery. There is no inherent provision for automatic rerouting or failover in the event of a failure, which can lead to longer downtimes and manual intervention for restoration. As such, while SDH networks offer enhanced operational features like comprehensive network management and diagnostic tools, PDH networks do not inherently support these capabilities, making them less suited for environments where high availability and reliability are critical.
The operational resilience of SDH, combined with its advanced diagnostic and management capabilities, renders it an invaluable framework for today’s backbone networks and critical infrastructures, where uninterrupted service and rapid fault correction are not just beneficial but essential.
Similarities of PDH and SDH
Despite their differences, PDH (Plesiochronous Digital Hierarchy) and SDH (Synchronous Digital Hierarchy) share several fundamental similarities that contribute to their widespread use in telecommunications. Both technologies employ Time-Division Multiplexing (TDM) to aggregate multiple digital data channels onto a single transmission medium. This multiplexing technique allows them to efficiently utilize existing telecommunications infrastructure by sharing physical pathways.
Moreover, both PDH and SDH adhere to established communication protocols, which facilitates their compatibility and interoperability with a variety of equipment from different vendors. This standardization has ensured that both technologies can be seamlessly integrated into existing networks, allowing for easier maintenance and upgrades.
Additionally, the wide support from equipment manufacturers means that network designers have flexibility in choosing components and planning for network expansions or enhancements.
Conclusion
The choice between PDH or SDH should be based on specific requirements such as capacity, future scalability, resiliency, delay variance, topology, and services. PDH is a simpler and more economical technology that is suitable for small-scale networks with low bandwidth requirements and low delay variance tolerance, whereas SDH is more advanced, flexible, resilient, and versatile.


