EPON Definition
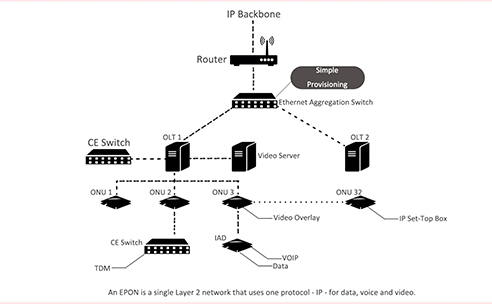
EPON (Ethernet passive optical network) is a technology that enables Internet, voice, and video access through the use of Ethernet packets instead of ATM cells, setting it apart from GPON. EPON operates as a point-to-multipoint network and supports symmetrical 1 Gbps upstream and downstream speeds in FTTH and FTTP deployments.
One of the advantages of EPON is its seamless interoperability with other Ethernet standards when connected to Ethernet-based networks on both ends. It eliminates the conversion or encapsulation processes. Additionally, EPON utilizes the same Ethernet frame with a payload capacity of up to 1518 bytes. Unlike other Ethernet versions, EPON does not rely on the CSMA/CD access technique. As Ethernet is widely adopted in local-area networks and metro-area networks, no protocol conversion is necessary.
For higher bandwidth requirements, there is a 10-Gbit/s Ethernet variant known as 802.3av. It operates at an actual line rate of 10.3125 Gbits/s and supports symmetrical 10 Gbits/s upstream and downstream speeds. Another variant combines 10 Gbits/s downstream with 1 Gbits/s upstream. By leveraging different optical wavelengths, specifically 1575 to 1580 nm downstream and 1260 to 1280 nm upstream, the 10-Gbit/s systems can be wavelength multiplexed alongside standard 1-Gbit/s systems on the same fiber.
Advantages of EPON
High Bandwidth:
EPON offers high bandwidth transmission capabilities, typically providing speeds of 1 Gbps or 2.5 Gbps. In theory, EPON supports a maximum speed of 10 Gbps, but currently, mainstream commercial devices support speeds like 1 Gbps or 2.5 Gbps, with future advancements expected to support higher speeds. It allows users to enjoy high-speed internet access, HD video streaming, online gaming, and other applications, meeting the high bandwidth requirements of modern communication needs.
Long Transmission Distance:
EPON networks can cover longer transmission distances, usually reaching over 20 kilometers and even up to 60 kilometers. This is due to the advantages of optical fiber, which is not susceptible to electromagnetic interference. In comparison, traditional copper cables have limited transmission distances, while EPON, through the use of optical fiber, can better support long-distance communication requirements.
Flexibility and Scalability:
EPON networks possess flexibility and scalability, allowing for easy addition or removal of users based on demand. It enables network operators to adjust the network’s scale according to user growth or reduction, reducing the costs of network deployment and maintenance.
Shared Bandwidth:
EPON utilizes Time Division Multiple Access (TDMA) technology to share bandwidth among different Optical Network Units (ONUs). The shared bandwidth could efficiently utilize network resources, ensuring users can obtain good network performance even during high-load periods.
Simplified Network Architecture:
EPON networks adopt a simple two-tier structure, where the Optical Line Terminal (OLT) connects multiple ONUs to achieve LAN aggregation. It makes network deployment and management more convenient.
Cost-Effectiveness:
Compared to traditional copper-based networks, EPON networks have cost advantages. Optical fiber transmission does not require power and has a long lifespan, effectively reducing operational costs. Additionally, EPON networks have strong scalability, allowing for the efficient utilization of resources to meet user growth, thereby increasing utilization rates and lowering costs.
Conclusion
EPON (Ethernet Passive Optical Network) has many advantages in terms of high bandwidth, long transmission distance, flexibility and scalability, shared bandwidth, simplified network architecture, and cost-effectiveness. Its advantages make EPON widely used in the field of modern communications and provide users with high-speed and reliable network connections.


