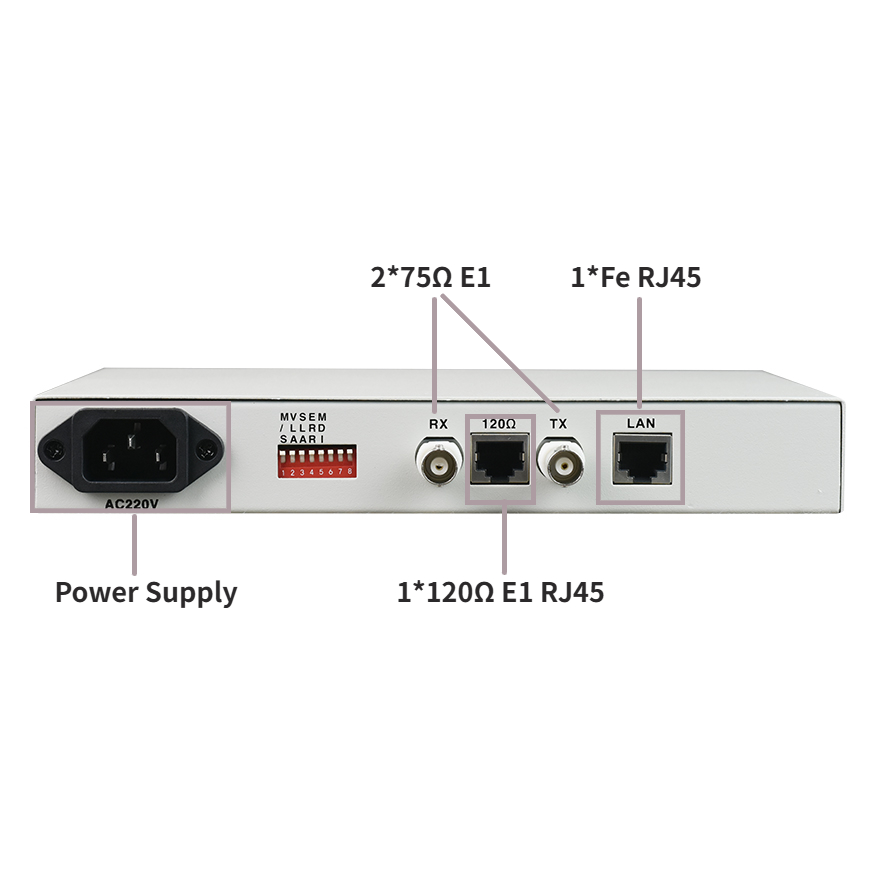
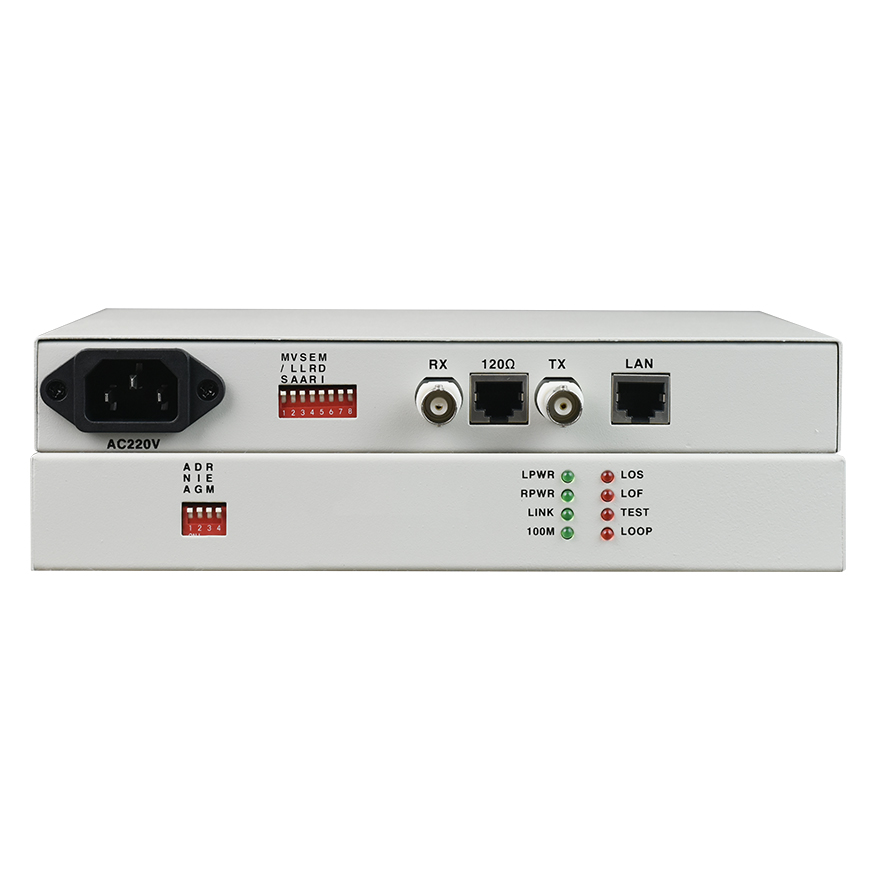
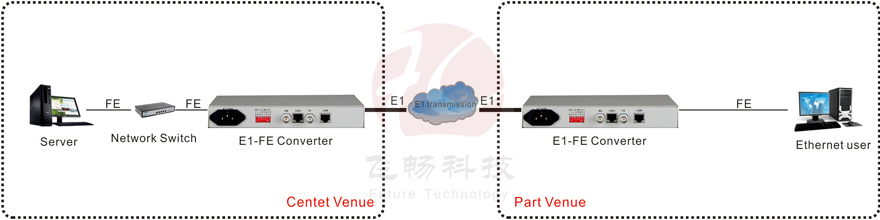
● The Ethernet to E1 converter supports unframed mode (2048K) with flexible application and the ability to manage the status of remote devices. Network management data does not occupy user business time slots.
● Can detect the E1 loopback with an indicator light. During loopback, packets with the same source and destination MAC addresses will not be sent to the Ethernet port to prevent switch crashes.
● Can differentiate between remote device power loss and E1 disconnection during signal loss.
● E1 failover function, which can be set not to send LINK signals to the Ethernet interface when an E1 line fault occurs.
● Supports jumbo frames with a maximum length of 2036 bytes.
● Built-in dynamic Ethernet MAC address list (4096 entries) and local data frame filtering function.
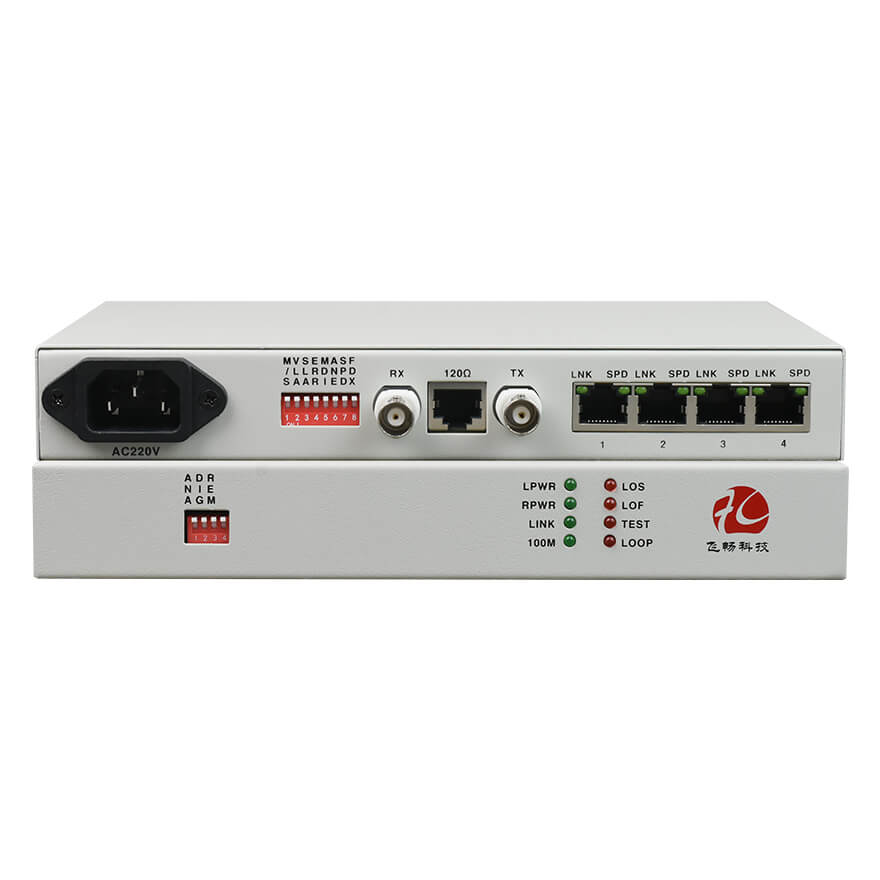
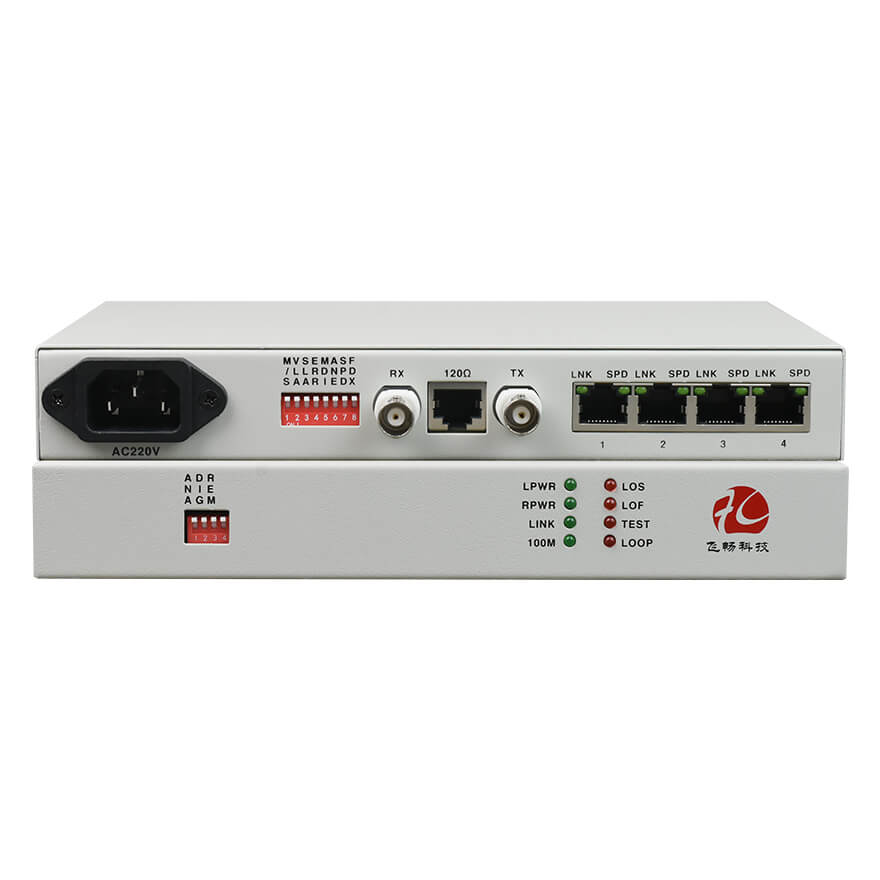
● Supports 10M/100M Ethernet interfaces, half/full duplex auto-Negotiation, VLAN protocols, and AUTO-MDIX (auto-negotiation of crossover and straight-through connections).
● It has an internal Ethernet data monitoring auto-reset function to prevent device crashes.
● 2 clock modes are available: E1 master clock and E1 line slave clock.
● Can force the remote device’s speed to follow the local device’s speed (not applicable in unframed mode).
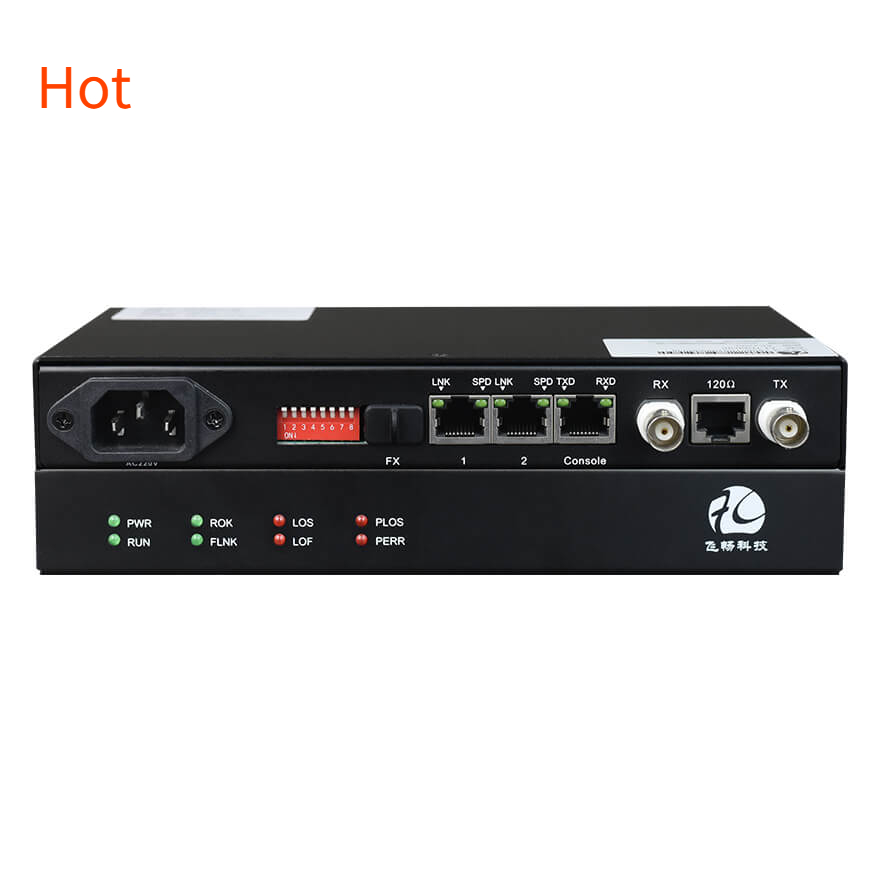
● 3 loopback modes: E1 local loopback (ANA), Ethernet local loopback (DIG), and remote Ethernet loopback (REM).
● Supports both 120Ω/balanced and 75Ω/unbalanced impedances without requiring additional configuration.
● Monitor and set temperature alarm thresholds and monitor the voltage and temperature of local and remote devices.
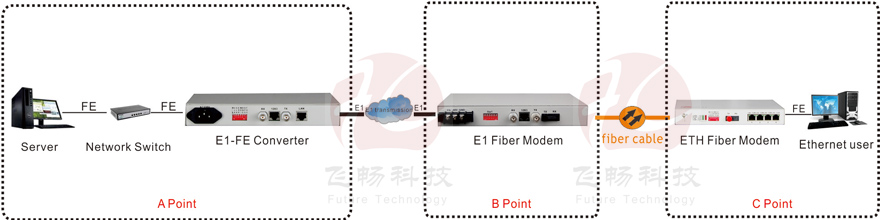
● Can form a topology structure: Ethernet E1 bridge (A) – E1 fiber modem (B) – Ethernet fiber modem (C).
● Can form a topology structure: Ethernet E1 bridge (A) – optical Ethernet E1 bridge (B) – Ethernet fiber media converter (C), with management capability at points B and C from point A.